Plumbing Systems & Codes: Essential Knowledge for Installation and Compliance
Plumbing systems and codes form the backbone of safe, efficient, and compliant building infrastructure. These systems distribute clean water, remove waste, and protect public health, while plumbing codes establish the standards that ensure proper installation and operation. Whether you’re a professional contractor, licensed plumber, or homeowner planning renovations, understanding these systems and regulations is crucial for avoiding costly mistakes, ensuring safety, and maintaining compliance with local authorities.
Explore our comprehensive Plumbing Guide for additional resources on fixtures, repairs, and maintenance beyond the systems and codes covered here.
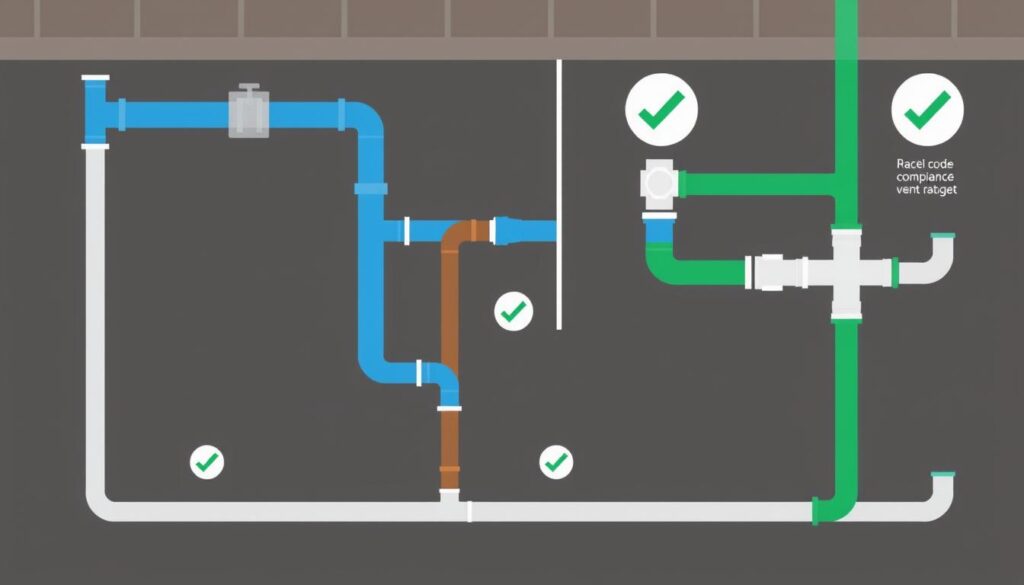
Why Plumbing Systems & Codes Matter
Plumbing codes are more than just bureaucratic requirements—they’re essential safeguards that protect public health and safety. These regulations ensure that plumbing systems are designed and installed to prevent contamination of drinking water, provide adequate drainage, and maintain proper sanitation. Without these standards, we risk exposure to waterborne diseases, structural damage from leaks, and inefficient water usage.
“Plumbing codes establish minimum standards for the design, construction, installation, alteration, and repair of plumbing systems. Understanding these codes makes it easy to ensure that your plumbing stays compliant with the law.”
For professionals, code compliance is non-negotiable—violations can result in failed inspections, project delays, fines, and even license suspension. For homeowners, understanding these systems helps you make informed decisions, communicate effectively with contractors, and ensure your home’s plumbing meets safety standards.
Plumbing Systems & Drainage
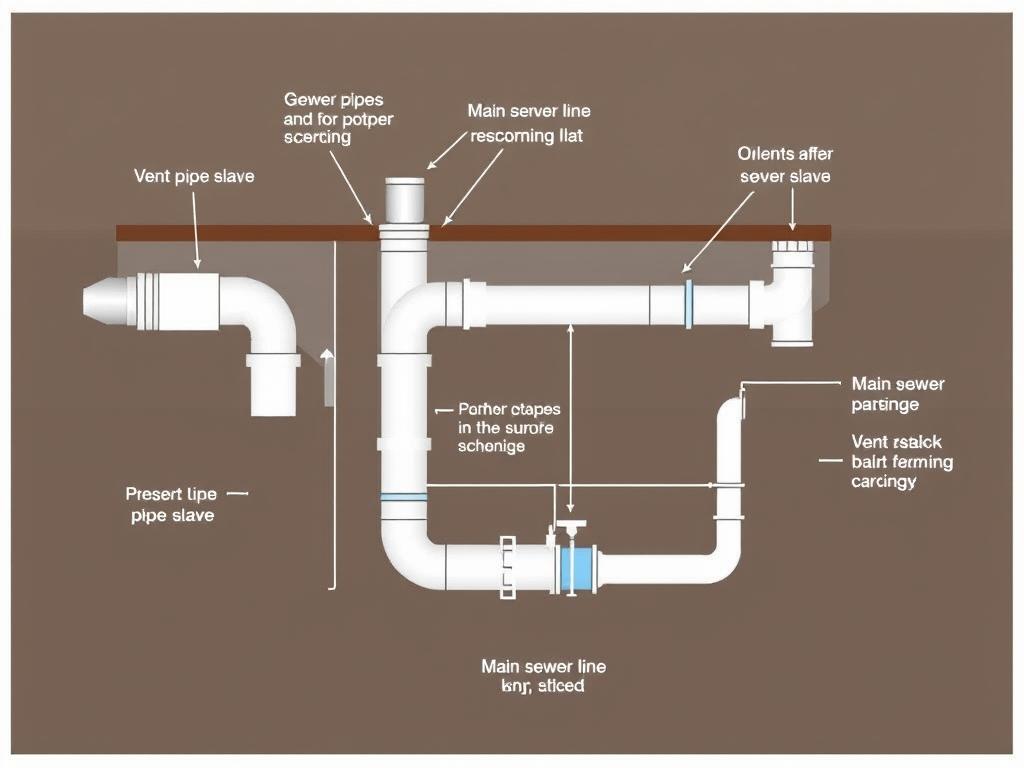
Effective plumbing systems rely on properly designed drainage networks that safely remove wastewater while preventing sewer gases from entering living spaces. These systems include drain pipes, vents, traps, and connections that must be sized and installed according to specific code requirements.
Key Components of Drainage Systems
- Drain pipes with proper slope (typically 1/4" per foot)
- Vent stacks that equalize pressure and release gases
- P-traps that create water seals to block sewer gases
- Cleanouts for maintenance access
- Backflow prevention devices
Common Drainage Requirements
- Minimum pipe diameters based on fixture units
- Maximum distances between fixtures and vents
- Proper support spacing for horizontal runs
- Approved materials for specific applications
- Testing procedures for system verification
Explore Drainage Systems in Detail
Discover comprehensive guides on proper installation techniques, code requirements, and troubleshooting for plumbing drainage systems.
Plumbing Codes & Regulations
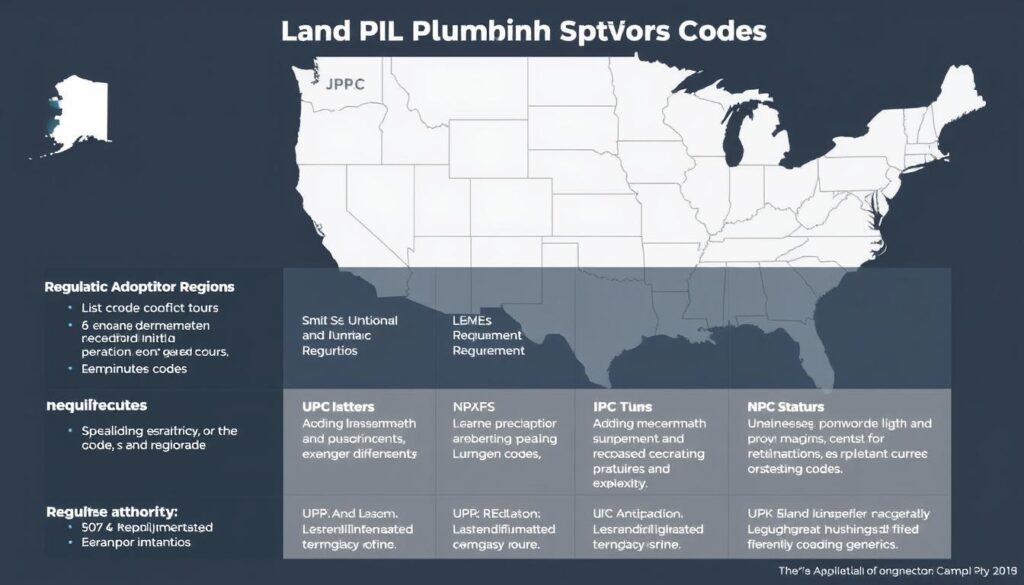
The United States utilizes several different plumbing codes depending on location. Understanding which code applies to your region is essential for compliance and successful project completion. These codes are regularly updated to incorporate new technologies, safety standards, and environmental considerations.
Major Plumbing Codes in the United States
| Code | Publishing Organization | Primary Regions | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC) | International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO) | Western United States | Prescriptive requirements, detailed specifications |
| International Plumbing Code (IPC) | International Code Council (ICC) | Midwest, Southeast, Northeast | Performance-based approach, design flexibility |
| National Standard Plumbing Code (NSPC) | Plumbing-Heating-Cooling Contractors Association | Northeastern United States | Balance of prescriptive and performance requirements |
Key Regulatory Considerations
Health & Safety
Regulations for backflow prevention, cross-connection control, and water quality protection
Installation Standards
Requirements for pipe sizing, support, materials, and joining methods
Inspection Processes
Procedures for verification, testing, and approval of plumbing installations

Master Plumbing Codes & Regulations
Access detailed explanations of code requirements, updates, and jurisdiction-specific information to ensure your projects meet all necessary standards.
Plumbing Wall Dimensions
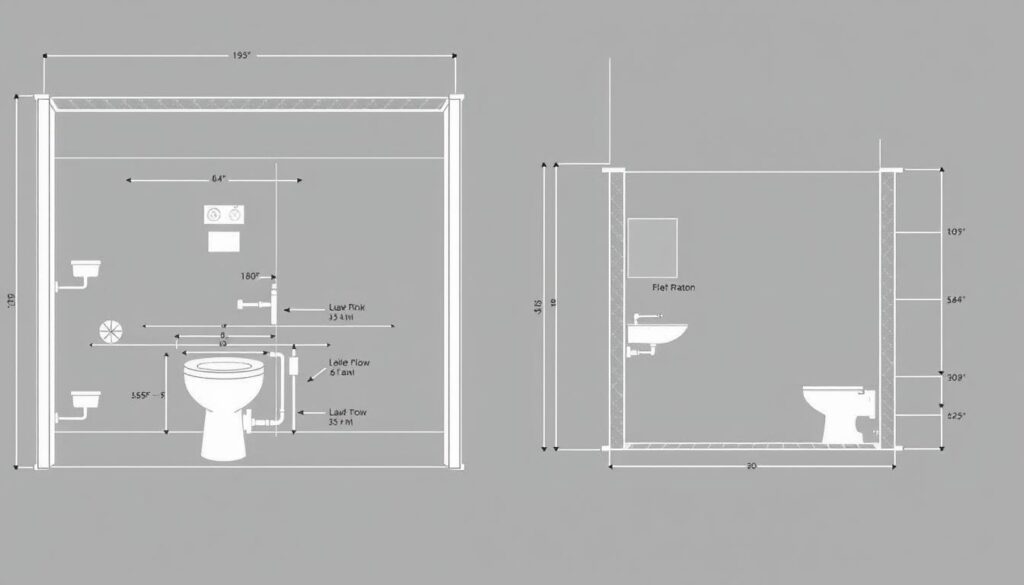
Proper plumbing wall dimensions are critical for successful installations. These specifications ensure adequate space for pipes, proper fixture placement, and accessibility for maintenance. Code requirements dictate minimum clearances, support structures, and protection measures for plumbing within walls.
Standard Wall Requirements
- Minimum wall thickness for different pipe types
- Required clearances around fixtures
- Access panel dimensions and placement
- Fire-stopping requirements for penetrations
- Structural considerations for load-bearing walls
Common Fixture Rough-in Dimensions
- Toilet: 12" from finished wall to center of flange
- Shower drain: 15-20" from each wall in corner installations
- Vanity sink: 20" from floor for standard height
- Bathtub: Specific manufacturer requirements
- Kitchen sink: 24" from floor to drain centerline

Get Precise Wall Dimensions
Find detailed specifications, diagrams, and code requirements for plumbing walls in various applications.
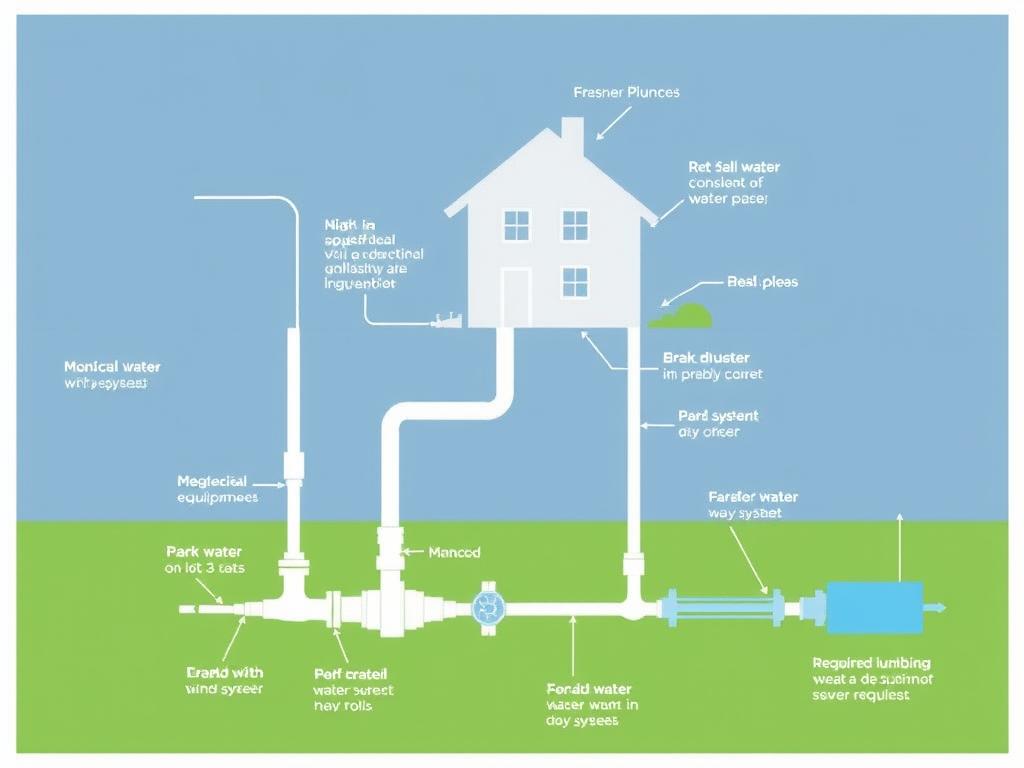
Plumbing Utilities
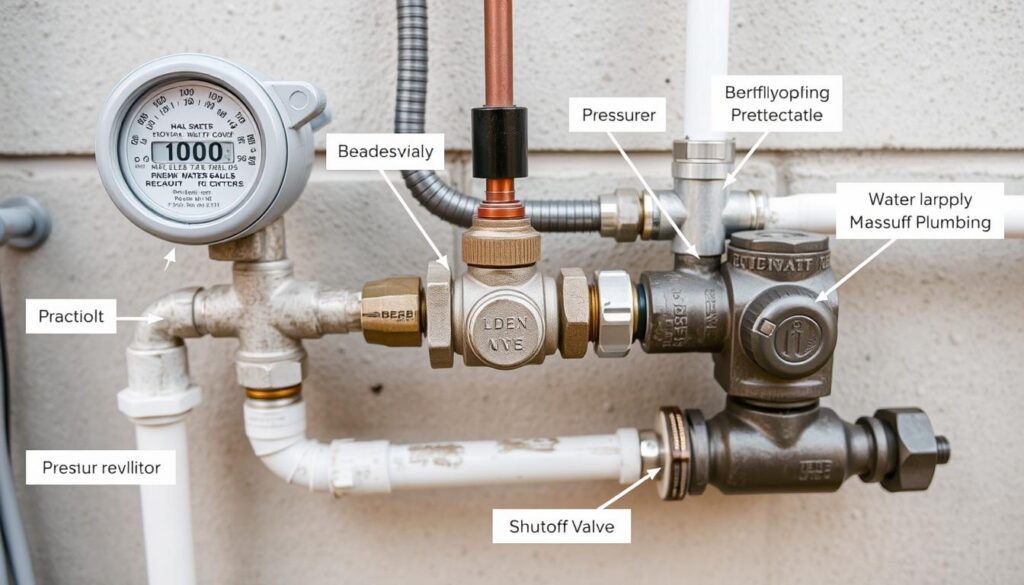
Plumbing utilities encompass the connections, equipment, and services that supply water to buildings and remove waste. These systems must interface correctly with municipal infrastructure while meeting code requirements for safety, accessibility, and performance.
Essential Utility Components
Water Supply
- Water meters and main shutoffs
- Pressure regulators
- Backflow prevention assemblies
- Service line materials and sizing
Waste Removal
- Sewer connections and cleanouts
- Septic systems (where applicable)
- Ejector pumps for below-grade fixtures
- Grease interceptors (commercial)
Special Systems
- Rainwater harvesting
- Greywater recycling
- Water treatment equipment
- Fire suppression connections
Understand Plumbing Utilities
Learn about utility connections, requirements, and best practices for integrating building plumbing with municipal systems.
Ensuring Code Compliance

Achieving code compliance requires attention to detail throughout the planning, installation, and inspection processes. Following these best practices helps ensure your plumbing systems meet all applicable regulations and pass inspection the first time.
Compliance Best Practices
- Verify which code applies in your jurisdiction
- Obtain proper permits before starting work
- Use only approved materials and methods
- Schedule inspections at required intervals
- Document all installations with photos
- Keep records of approvals and certifications
Common Compliance Pitfalls
- Avoid These Mistakes
- Improper pipe sizing or slope
- Inadequate venting arrangements
- Missing access panels for maintenance
- Incorrect fixture clearances
- Mixing incompatible materials
- Failing to protect pipes from damage

Additional Resources
Code Publications
- Uniform Plumbing Code (UPC)
- International Plumbing Code (IPC)
- National Standard Plumbing Code (NSPC)
- State-specific amendments
Professional Organizations
- International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials (IAPMO)
- Plumbing-Heating-Cooling Contractors Association
- American Society of Plumbing Engineers
- Local plumbing associations
Training Resources
- Code certification courses
- Continuing education programs
- Online tutorials and webinars
- Manufacturer installation guides

Navigate the World of Plumbing Systems & Codes
Understanding plumbing systems and codes is essential for anyone involved in building construction, renovation, or maintenance. By familiarizing yourself with these regulations and best practices, you can ensure safe, efficient, and compliant installations that protect public health and property.
Explore Our Complete Plumbing Guide
Discover comprehensive resources on all aspects of plumbing, from fixtures and repairs to systems and codes.
How often are plumbing codes updated?
What are the penalties for non-compliance with plumbing codes?
